Vertikal knogleopbygning af den atrofiske posteriore mandibel før implantatindsættelse ved hjælp af sandwich-osteotomi
I nærværende oversigtsartikel præsenteres den nuværende viden om vertikal knogleopbygning af den atrofiske posteriore mandibel før implantatindsættelse ved hjælp af sandwich-osteotomi, og den kirurgiske procedure illustreres.
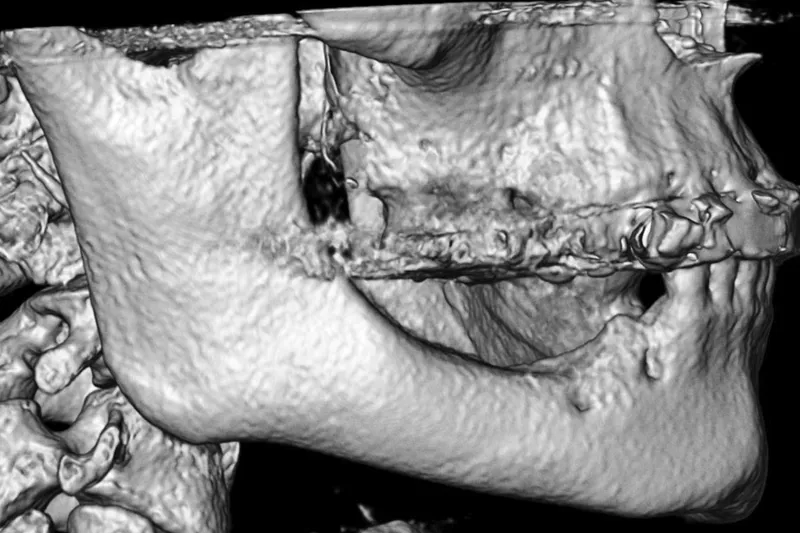
Sufficient højde og bredde af processus alveolaris er en forudsætning for at sikre optimal implantatplacering i kæbeknoglen og etablere grundlaget for en æstetisk og funktionel udformning af den protetiske erstatning med god langtidsprognose. Imidlertid kan implantatindsættelse i den atrofiske posteriore mandibel være umulig eller vanskelig som følge af reduceret afstand fra toppen af processus alveolaris til den øvre begrænsning af canalis mandibulae. Vertikal knogleopbygning af processus alveolaris’ højde før implantatindsættelse ved hjælp af sandwich-osteotomi og interpositionelt transplantationsmateriale foretages almindeligvis, når højden af processus alveolaris ikke tillader protetisk rehabilitering med korte eller standardlængdeimplantater, men hvor knoglehøjden muliggør en kraniel forskydning af processus alveolaris over canalis mandibulae. Langtidsundersøgelser og systematiske oversigtsartikler har vist høj overlevelse af suprastruktur og implantat, begrænset periimplantært marginalt knogletab, forudsigelig vertikal knogleopbygning af processus alveolaris og relativt få komplikationer efter sandwich-osteotomi med anvendelse af interpositionelt transplantationsmateriale. I nærværende oversigtsartikel præsenteres den nuværende viden om vertikal knogleopbygning af den atrofiske posteriore mandibel før implantatindsættelse ved hjælp af sandwich-osteotomi, og den kirurgiske procedure illustreres.
Klinisk relevans:
Implantatindsættelse i den atrofiske posteriore mandibel er ofte vanskelig eller umulig som følge af reduceret afstand fra toppen af processus alveolaris til den øvre begrænsning af canalis mandibulae. Indsættelse af korte implantater, vertikal knogleopbygning før implantatindsættelse ved hjælp af sandwich-osteotomi samt lateralisering eller transpositionering af n. alveolaris inferior er de hyppigst anvendte kirurgiske teknikker til protetisk rehabilitering af den atrofiske posteriore mandibel. Sandwich-osteotomi med anvendelse af et interpositionelt transplantationsmateriale foretages almindeligvis, når højden af processus alveolaris ikke tillader protetisk rehabilitering med korte implantater, men muliggør en vertikal forskydning af processus alveolaris over canalis mandibulae, således korte eller standardlængdeimplantater efterfølgende kan indsættes.Vertical bone augmentation of the atrophic posterior mandible prior to implant placement with the use of sandwich osteotomy
Sufficient height and width of the alveolar ridge is a prerequisite to ensure optimal implant placement for a correct aesthetic and functional prosthetic solution with a good long-term prognosis. However, placement of implants in the atrophic posterior mandible may be impossible or difficult due to reduced distance from the top of the alveolar ridge to the upper border of the mandibular canal. Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation prior to implant placement with the use of sandwich osteotomy technique and placement of an interpositional grafting material is therefore commonly performed when the height of the alveolar ridge does not allow prosthetic rehabilitation with short or standard-length implants but permits cranial displacement of the alveolar ridge above the mandibular canal. Long-term studies and systematic reviews have revealed high survival of suprastructures and implants, limited peri-implant marginal bone loss, predictable vertical bone gain and relatively few complications following the use of sandwich osteotomy technique with an interpositional grafting material. In the present review, the current knowledge on vertical alveolar ridge augmentation of the atrophic posterior mandible with the use of sandwich osteotomy prior to implant placement is presented and the surgical procedure is illustrated.