Bonding ceramic restorations
Blandt de klinisk relevante parametre, der er involveret i valg af et adhæsivt cementsystem til binding af keramiske restaureringer til tandens hårde væv, skal æstetik, farvestabilitet, brugervenlighed og arbejdstid nævnes.
BINDING AF KERAMISKE RESTAURERINGER
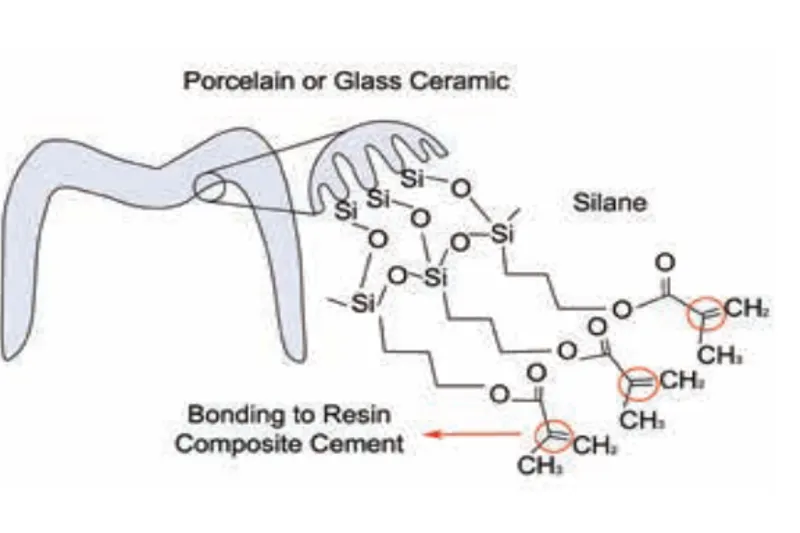
Restaureringer af porcelæn og glaskeramik forstærkes ved binding til tænderne: I følge litteraturen opnås de bedste resultater ved forbehandling af disse keramikkers overflade med flussyre efterfulgt af applicering af silan eller keramisk primer, og derefter cementering med en lyshærdende eller kemisk hærdende plastcement. Plastcementtypen er afhængig af restaureringens tykkelse. For restaureringer fremstillet af zirkoniumdioxid anbefales det, at overfladen gøres ru ved gritblæsning med korund partikler før cementering med en adhæsiv plastcement. En alternativ forbehandling af zirkoniumdioxidrestaureringer er silikatisering, efterfulgt af applicering af silan, som har til formål at øge vedhæftningen af plastcementen til keramikken. Den bedste og mest holdbare binding af zirkoniumdioxidrestaureringer opnås ved at anvende en dualhærdende, adhæsiv plastcement, som indeholder fosfatestergrupper. Blandt de klinisk relevante parametre, der er involveret i valg af et adhæsivt cementsystem til binding af keramiske restaureringer til tandens hårde væv, skal æstetik, farvestabilitet, brugervenlighed og arbejdstid nævnes.
Clinical relevance:
Bonding to dental ceramics requires great care and attention to fine detail. Manufacturers’ instructions are to be followed. Appropriate surface pretreatment of the ceramics, as well as the selection of an appropriate adhesive cement system, are needed to ensure optimal and durable bonding. This said, deep knowledge of dental materials contributes to the delivery of good treatment practice.
Porcelain and glass ceramics need to be bonded to teeth for the reinforcement of restorations: according to studies, the best results are achieved by pretreating and etching the ceramic surface with hydrofluoric acid, then applying a silane coupling agent or a ceramic primer, and luting with a lightor dual-cured adhesive cement, depending on the restoration thickness. Zirconia is bonded to teeth after gentle roughening by airborne abrasion (gritblasting) using an adhesive resin composite cement. In addition, Tribochemical silica coating combined with silane application is an alternative that might provide enhanced adhesion to zirconia. The best durable bonding to zirconia is achieved by applying a dual-cured adhesive resin composite cement that contains phosphate ester groups. Among the clinically relevant parameters involved in choosing an adhesive cement system to bond ceramic restorations to the dental hard tissues, the aesthetic properties, colour stability, ease of handling, and appropriate working times of the cement are to be considered.