Digitale arbejdsgange ved virtuelt planlagt computerguidet implantatindsættelse
Denne oversigtsartikel beskriver de digitale arbejdsgange ved planlægningen og udførelse af guidet implantatindsættelse ved hjælp af individuelt fremstillede styreskinner i to udvalgte patienttilfælde.
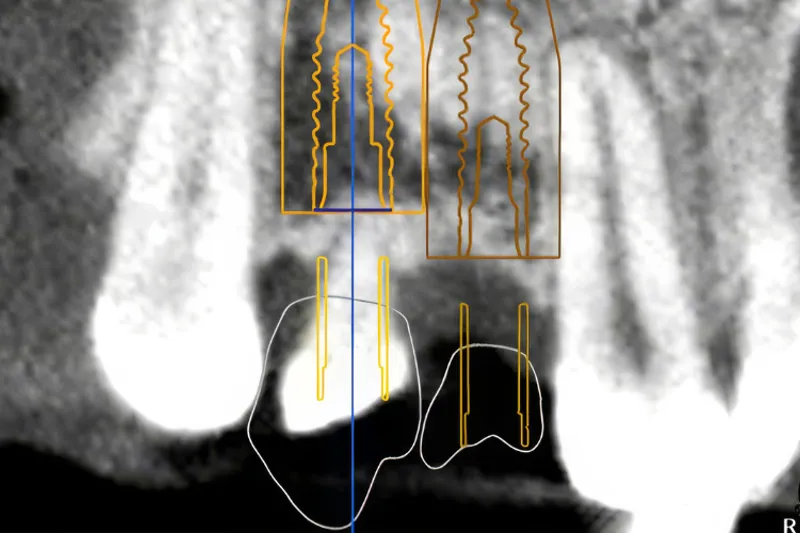
Tilstrækkelig højde og bredde af processus alveolaris er en forudsætning for at opnå en optimal tredimensionel implantatplacering og etablere grundlaget for en korrekt æstetisk og funktionel udformning af den efterfølgende protetiske rekonstruktion med en god langtidsprognose. Prøvetandsopstilling og styreskinner kan anvendes for at hjælpe til en optimal implantatplacering. Udvikling af softwareprogrammer har gjort det muligt at simulere den endelige protetiske rekonstruktion og implantatplacering samt udforme styreskinner, der intraoperativt kan assistere til udboring af implantatlejet og implantatindsættelsen. Imidlertid er guidet implantatindsættelse behæftet med risiko for fejl i forbindelse med databearbejdning, behandlingsplanlægning, printtekniske faktorer og intraoperativ forskydning af styreskinnen, som hver især kan have afgørende betydning for præcisionen af implantatbehandlingen. Implantatets placering anbefales derfor med en sikkerhedsmargin på 2 mm til nærliggende anatomiske strukturer og nabotænder. Guidet implantatindsættelse baseres på en grundig vurdering af patientens individuelle behov, behandlingens kompleksitet, anatomiske overvejelser og behandlerens erfaring og ekspertise med teknologien. Denne oversigtsartikel beskriver de digitale arbejdsgange ved planlægningen og udførelse af guidet implantatindsættelse ved hjælp af individuelt fremstillede styreskinner i to udvalgte patienttilfælde.
Klinisk relevans:
Uhensigtsmæssig implantatplacering kan vanskeliggøre eller umuliggøre fremstilling af en optimal protetisk rekonstruktion og medføre risiko for besværet renhold, mucositis og periimplantitis samt risiko for tidligt eller sent tab af implantat. Endvidere kan afvigelser under implantatudboring medføre beskadigelse af nærliggende anatomiske strukturer og nabotænder. Udførlig klinisk og radiologisk undersøgelse før implantatindsættelse er således nødvendigt for at opnå et sikkert og forudsigeligt behandlingsresultat. Guidet implantatindsættelse og fremstilling af en styreskinne kan i udvalgte patienttilfælde hjælpe til en optimeret implantatplacering.
Digital workflow in guided implant surgery
Sufficient height and width of the alveolar process is a prerequisite to ensure an optimal three-dimensional implant placement for a correct aesthetic and functional design of the subsequent prosthetic reconstruction with a good longterm prognosis. A dental mock-up and surgical guide can be used to assist in optimal implant placement. Furthermore, emerging of software programs has made it possible to simulate the final prosthetic reconstruction and implant placement, as well as the design of guide templates that can assist during implant bed preparation and implant placement. Guided implant surgery is associated with a risk of errors in data processing, treatment planning, technical printing conditions, and intraoperative displacement of the guide, each of which can have a crucial impact on the precision of the implant placement. Therefore, implant placement should be planned with a safety margin of 2 mm to adjacent anatomical structures and teeth. Guided implant surgery should be based on a thorough assessment of the patient's individual needs, the complexity of the treatment, anatomical considerations, and the clinician's experience and expertise with the technology. This article describes an overview of the digital workflow in the planning and execution of guided implant placements using individually manufactured guides in two selected patients.

